Last updated: Tuesday, January 21, 2025
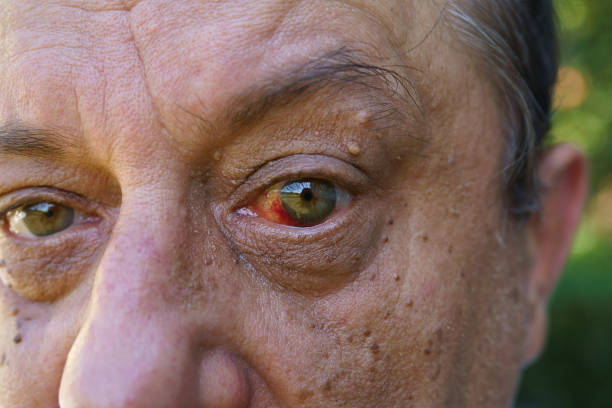
In medicine, an outstretched eyeball is called a proptosis. Cancer and thyroid issues frequently cause bulging eyes. Addressing the root cause is a common component of management. Proptosis can result from a variety of medical conditions, but thyroid eye disease (TED) is the most common cause of it. Other possible causes of protruding eyes include injuries, tumours, and infections. Depending on what causes it, proptosis can affect one or both of the eyes. When two eyes protrude, it's called bilateral proptosis and when only one does it's called unilateral proptosis.
What Is Proptosis?
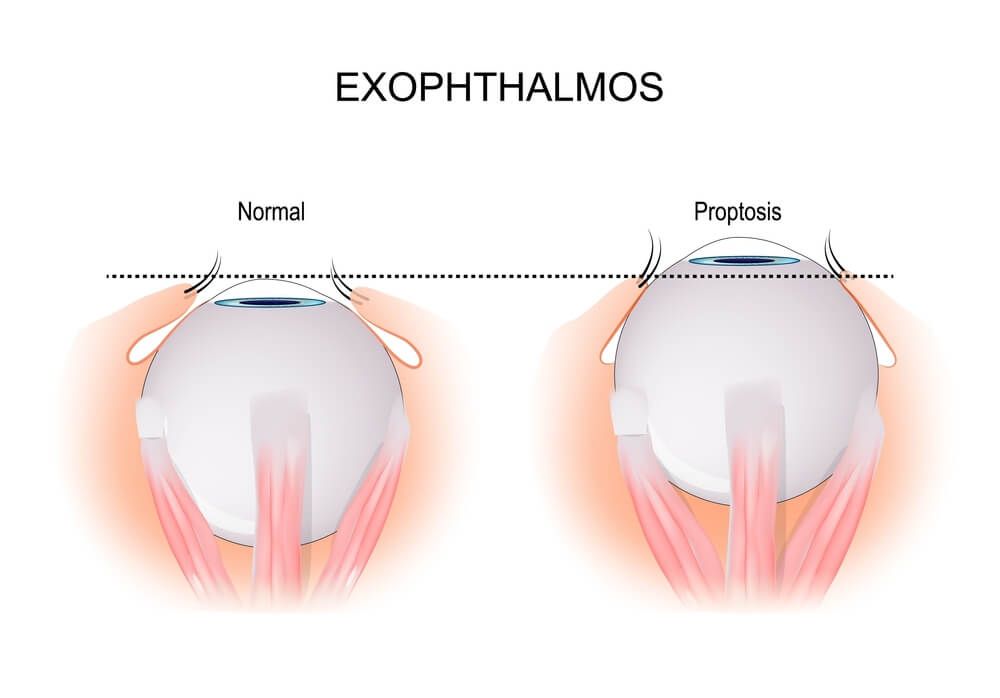
When one or both of your eyes protrude, it's called eye proptosis. A diagnosis of proptosis typically entails an eye protrusion measuring more than 2 millimetres. Exophthalmos, which translates from Greek to mean bulging eyes is another name for proptosis. A similar-sounding condition called buphthalmos is named after the Greek words meaning Ox-eyed. An eye that is larger than average at birth or soon after is known as buphthalmos. Congenital glaucoma is the most frequent cause of it.
Many conditions can lead to proptosis eye but the most common ones are hormone-related ones.
Thyroid Eye Diseases (Ted)
TED an autoimmune disease is the most common cause of proptosis in one or both eyes and other problems related to the eyes. People with proptosis in one eye who have hyperthyroidism or abnormally elevated thyroid hormone levels make up about one in three. The cause of abnormal hormone levels is found in about 90% of cases of bilateral proptosis.
Approximately 90% of individuals with TED suffer from Graves disease, an autoimmune disorder associated with hyperthyroidism. According to estimates, 1 in 4 Graves disease patients will experience TED. If TED is not treated optic nerve compression may result in impairing vision permanently. People with thyroid-related ocular diseases also experience retraction of the eyelids in over 90% of cases.
The upper or lower eyelid is pulled back at this point. Eye dryness may result from eyelid retraction in extreme situations where you cannot close your eyes completely. You run a higher risk of ulcers or infections in your eyes when you have dry eyes which can cause blindness.
Cancer
An early sign of primary cancers such as melanoma or carcinoma that begin to grow around your eyes is proptosis in one eye. Cancers that originated elsewhere may also spread to other parts of the body and cause bulging eyes. While not the only cause metastatic breast cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer-related proptosis. In a 2018 case report, a 40-year-old woman experienced headaches and proptosis as the initial signs of multiple myeloma a type of blood cancer.
Physical Injury
Proptosis can result from a wide variety of traumatic injuries. An earlier 2013 case report, for instance, detailed the development of proptosis in a 23-year-old football player whose helmet came loose and struck him in the right eye. A retrobulbar hematoma or accumulation of blood deep in the tissue between your eye and skull can be the result of trauma to your eye. This blood clot may cause your eye to bulge. Because air escapes your sinuses and gets into the area around your eye, breaking your skull around your eye may also result in proptosis.
Illnesses
Severe sinus infections can bring inflammatory disorders like orbital cellulitis or orbital abscesses. These inflammatory diseases can cause swelling behind your eyes which puts strain on the structure and may result in proptosis.
Blood Vessel Disease
Proptosis and other eye complications can result from abnormalities in your blood vessels caused by granulomatosis with polyangiitis, a rare autoimmune disease.
Which Symptoms Correspond To Ocular Proptosis?
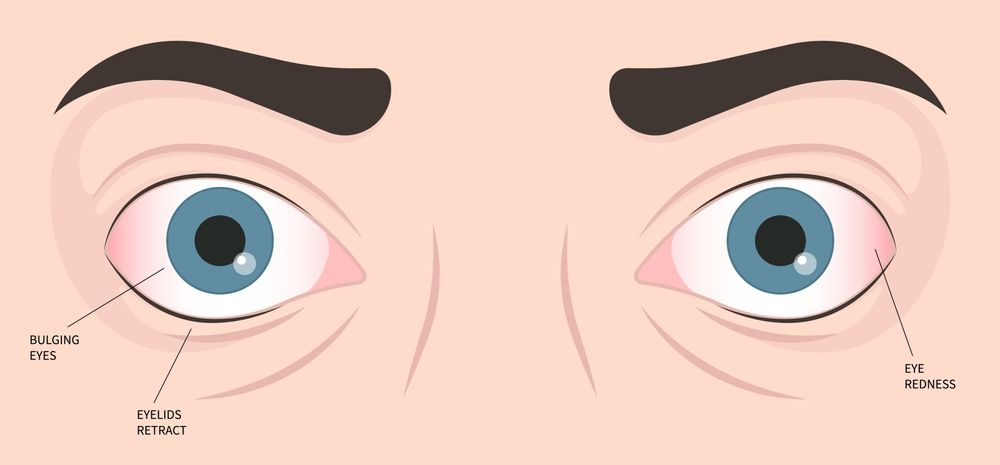
Your whitest area of the eyes is more noticeable when they protrude. Furthermore, your eyeballs protrude from their eye sockets. Your eyes appear wide open so you might see less of your upper eyelids. There are additional signs of a protruding eye that you might encounter.
- A scratchy feeling in your eye.
- Epiphora or dry itchy or wet eyes.
- Swelling or redness of the eyelids.
- Tightness in your muscles that could keep you from moving your eyes.
- Light sensitivity.
- Headache.
- Temperature spike.
What Disease Causes Bulging Eyes?
An autoimmune disease in which your body's immune system targets cells in your thyroid gland and the tissue behind your eyes is the most common cause of protruding eyes. Thyroid eye disease (TED) is the term used to describe proptosis in individuals with thyroid conditions. The most common cause of protruding eyes is thyroid dysfunction.
Some Proptosis Causes Are:
Graves Disease
The condition known as Graves disease hyperthyroidism or thyroid eye disease is brought on by an overabundance of thyroid hormone production. This condition can have a wide range of symptoms and typically requires an ENT doctor to diagnose. The eye tissues may occasionally swell in Graves disease forcing the eyes forward and resulting in proptosis. Medication can assist in regulating the thyroid in these situations. In more extreme situations, orbital decompression may be required to open up the eye socket and restore normal eye function. Because the eyelids might not close completely exposing the cornea, these cases may present a unique risk to the eyes.
Orbital Tumor
Hemangiomas, carcinogenic tumours, and malignant tumours can all result in proptosis. Treatment must be given right away if a tumour is developing behind the eye which can result in swollen eyes. Radiation surgery or chemotherapy are often used as treatments for tumours inside, outside, or behind the eye.
Internal Injury
Ocular socket bleeding can happen with any kind of orbital trauma. This can force the eye forward as the blood-filled eye socket expands. Optic nerve damage is very likely to occur in these situations. You should see a doctor right away to relieve the pressure on the optic nerve and prevent blindness.
Orbital Cellulitis
Orbital cellulitis is the term for tissue inflammation in the orbits. Ocular bulging may be a consequence of orbital cellulitis. The sinuses or oral cavity are typically the source of the infection. On occasion, it may also result from an injury to the eyelid. A life-threatening infection can spread to the brain and other parts of the body in cases of orbital cellulitis. Antibiotics are typically used in treatment.
Inflammatory Response
A subset of inflammatory diseases is those that affect the body's organs and cause tissue inflammation. This may occasionally have an impact on the eye socket resulting in proptosis. One kind of illness that proptosis causes is an inflammatory orbital pseudotumor which does not involve cancer cells. Corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs can be used to treat orbital inflammation.
How Is The Treatment For Proptosis Administered?
The course of your treatment might involve:
- Artificial tears such as gel or drops to prevent corneal damage and relieve dry eyes.
- Antibiotics, If you are ill.
- Pharmaceutical therapies such as drugs for hyperthyroidism for underlying illnesses. IV drugs such as teprotumumab which treats thyroid eye disease or corticosteroids, which are anti-inflammatory drugs.
Are There Any Other Non-Surgical Treatments Available For Bulging Eyes?
Alternative forms of treatment could be:
- Prisms: that clip onto your glasses to refocus light as it enters your eyes are among the therapies for double vision.
- Immunosuppressive medications: These medications may mitigate the ocular effects of immune system assaults.
- Corticosteroids: To reduce swelling or improve vision you may receive steroids intravenously or through a vein in your arm.
Will Surgery Be Necessary For Me?
Surgery might be required for:
- Make more room in the eye socket behind your eye.
- Take care of double vision.
- If you cannot close your eyelids all the way, protect your corneas.
- Eliminate a tumour.
How Do I Know If I Have Big Eyes?
A thyroid gland issue may be indicated by swollen eyes or exophthalmos. Though it may affect your vision it can be treated so get checked out right away. Verify whether your eyes are swollen. Your eyes could be swollen if:
- It appears like you have more protrusion in your eyes than normal.
- Your eyes may appear to be open wide as there is less visibility of your upper eyelids.
- Your eye whites are more noticeable.
Depending on what causes eye bulging you may experience additional symptoms which could include:
- Discomfort or difficulties shutting or opening your eyes.
- The feeling of grit or dust in the eyes or dry eyes.
- When you stare at bright lights your eyes hurt.
How Can I Overcome Eyeball Out Of Socket?
Besides altering your appearance, protruding eyes can lower your self-esteem and boost your confidence. Your daily life might change in ways you didn't anticipate if it affects your vision. You might feel angry, nervous, or depressed because of these changes. Getting assistance from a social worker or mental health professional can improve your mood:
- Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) which is used by mental health professionals can assist you in developing coping mechanisms for negative thoughts and emotions.
- Social workers can help you find local resources in your community, such as support groups or online resources, if your vision problems prevent you from driving.
Bottom Line
A protruding eye is called proptosis in medicine. Proptosis is most frequently caused by thyroid disorders. Infections cancer and injuries to the eyes are additional causes. If you have proptosis, you must see an eye doctor. Bulging eyes may in extreme circumstances, result in irreversible vision loss. Your best chance of treating the underlying cause and reducing eye damage is to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
FAQ's
What are Bug Eyes
"Bug eyes" is a colloquial term for bulging or protruding eyes, medically known as proptosis or exophthalmos.
What Causes Bug Eyes in People?
The most common cause is thyroid eye disease, particularly associated with hyperthyroidism and Graves' disease.
What causes one eye bulging?
Bulging of one eye can result from bleeding, infection, inflammation, or tumors in the eye socket.
How to fix bulging eyes naturally?
While natural remedies like cool compresses can alleviate discomfort, addressing the underlying cause is essential. Consulting a healthcare provider is recommended for proper diagnosis and treatment.