Last updated: Tuesday, January 21, 2025
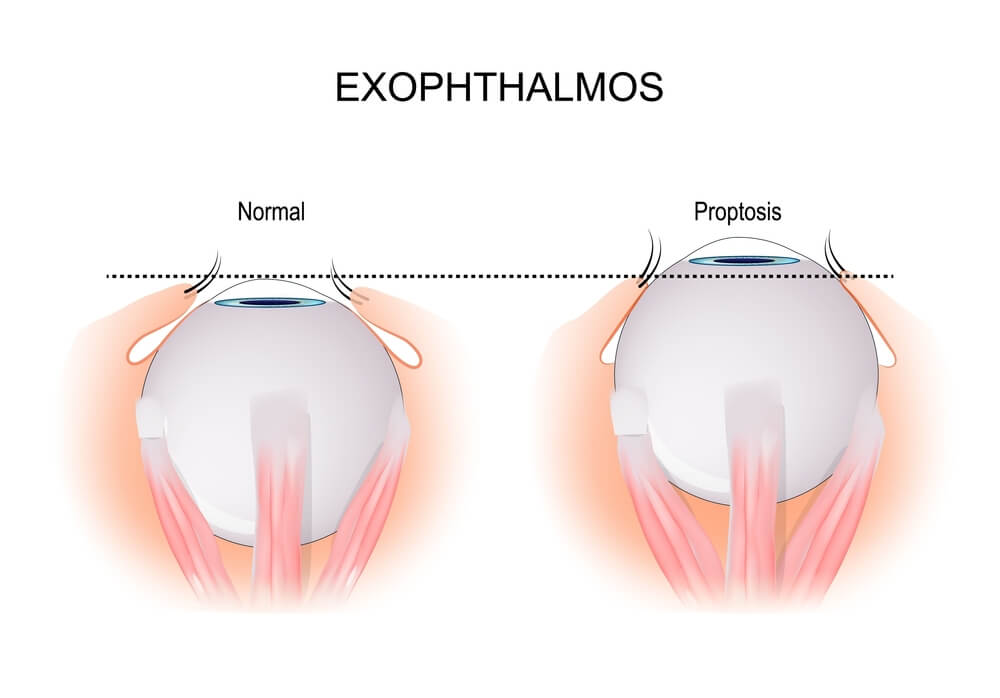
Protrusion of one or both eyes from their normal position within the eye sockets is a condition known as exophthalmos, also called proptosis or bulging eye. It's crucial to remember that exophthalmos is a symptom of an underlying disorder rather than a distinct medical condition. Graves disease, a thyroid condition that causes the thyroid gland to become overactive, is the most frequent cause of exophthalmos. Exophthalmos symptoms can range in intensity and may get better with time. If treatment is not received, the eyes may continue to enlarge, which could be uncomfortable and impair vision.
The Common Reasons for Exophthalmos: Thyroid Disorders and Graves Disease
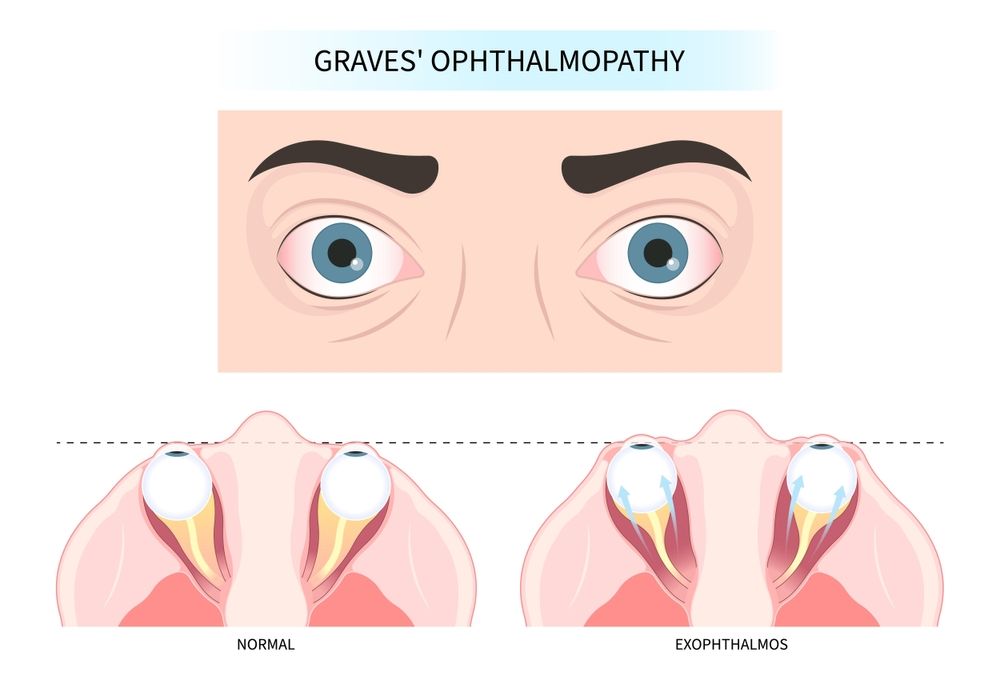
The thyroid gland is impacted by Graves' illness. The overproduction of thyroid hormones, known as hyperthyroidism, results from the immune system misattacking the thyroid gland in Graves disease. Exophthalmos or protruding eyes is one of the symptoms that can result from this excessive thyroid hormone production. The exact mechanism that causes the eyes to protrude from their sockets in Graves disease is exophthalmos, which is caused by swelling and inflammation of the tissues behind the eyes.
What Causes Exophthalmos?
Several underlying medical disorders that impact the tissues surrounding the eyes or the actual eye can also cause exophthalmos. Exophthalmos in children is most frequently caused by an infection (cellulitis) in or around the eye. The following are some additional possible exophthalmos causes:
- Shedding blood from the eyes.
- Cancers: Soft tissue sarcomas neuroblastoma etc.
- The Glaucoma.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma.
- A Hemangioma.
- The histocytosis1.
To receive the right care and management it's critical to identify the precise cause of exophthalmos with your healthcare provider.
Symptoms Associated With Exophthalmos
The following are signs of exophthalmos and Graves disease:
- Either of the eyes bulging or projecting.
- A scratchy dry or irritated feeling in the eyes.
- Puffiness or oedema surrounding the eyes.
- Seeing double or blurry.
- Pain or soreness in the eyes.
- Light sensitivity (photophobia).
- Having trouble shutting my eyelids all the way.
- Conjunctivitis or redness or inflammation of the eyes.
- Having difficulty moving your eyes when you look around.
The intensity of these symptoms might differ, and they might change over time. Patients suffering from Graves disease or exophthalmos should consult a physician for assessment and treatment to effectively manage symptoms related to the thyroid condition and the eyes.
Signs That Point To The Need For An Immediate Medical Assessment
If any of the above-mentioned bulging eye symptoms apply to you, consult your healthcare professional. They probably represent a more serious medical problem that needs to be addressed by a physician. Getting in touch with a medical expert is imperative if:
- You have enlarging eyes for no apparent reason.
- There are extra symptoms such as pain or fever that accompany bulging eyes.
Your doctor will perform a physical examination as well as ask questions about your medical history. They might inquire about things like:
- Does this affect both eyes?
- When did you discover the protrusion?
- Is the situation getting worse?
- Do you have any additional symptoms?
Exophthalmos Treatments?

There are several steps involved in exophthalmos treatment. Your doctor will inquire about the nature of your symptoms when they first appeared, any comorbidities, and your medical history in general. In addition, a comprehensive examination of your eyes will be performed, which will involve measuring the protrusion of your eyes, evaluating eye movement, and looking for any anomalies or signs of inflammation. Additional examinations could consist of:
- Visual acuity test: This can identify vision changes.
- Slit-lamp examination: This specialized eye exam looks for signs of eye disease or injury by closely examining the structures of the eye under a microscope equipped with a bright light.
- Imaging tests: These can be ordered to get precise images of the eye sockets and surrounding structures such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Thyroid hormone levels can be determined through blood tests. Graves disease and other thyroid conditions are frequently linked to exophthalmos. By following these diagnostic procedures your healthcare provider can identify the reason behind your protruding eyes and create a personalized treatment plan.
Taking Care of Exophthalmos
Thankfully, there are efficacious therapies accessible. While some self-care techniques don't require medication, others need to be suggested or prescribed by your healthcare professional. A surgical procedure might be required in certain situations. Depending on the underlying cause of your condition, there may be a variety of exophthalmos treatments available such as using artificial tears to lubricate and shield your corneas.
You can employ the following self-care techniques:
- If your eyes are sensitive, wear sunglasses to protect them from the sun. To get the best protection against the sun and wind wear wraparound sunglasses.
- Lubricating eye drops like artificial tears can relieve discomfort and dryness. If your eyelids don't close all the way, use a lubricating gel before going to bed to avoid dryness.
- Raise the head of your bed to release pressure points around your eyes which can help minimize puffiness and swelling.
- Your eye doctor might recommend prism-containing glasses if you experience double vision. Antibiotics are prescribed to treat infections if that's what's causing the problem.
Your healthcare provider must prescribe oral or intravenous corticosteroids for moderate-to-severe cases. Only a smaller percentage of exophthalmos patients need surgery. For eyes that bulge, there are various kinds of eye surgeries, including:
Surgery For Orbital Decompression
To make more room for the swollen tissues behind the eyes this procedure involves removing bone from the orbit of the eye socket. Orbital decompression surgery can relieve symptoms like puffy eyes and discomfort in the eyes by lowering the pressure inside the orbit.
Surgery For Strabismus
Strabismus surgery might be advised if protruding eyes cause diplopia or double vision because of misaligned eye muscles. By realigning the eyes this surgery minimizes double vision by rearranging the muscles around the eyes.
Elimination Of Orbital Fat
Through an incision inside the lower eyelid, excess fat from the eye socket is removed during this procedure. It can ease pressure on the eyes and lessen the appearance of bulging.
Exophthalmos Possible Complications
It may become more difficult for you to completely close your eyes if your exophthalmos progresses. The corneas, the transparent coverings that shield the front of your eyes may become dry because of this. Long-term corneal dryness raises the possibility of infections or ulcers which could impair vision if left untreated.
What Possibilities Are There for a Person with Exophthalmos?
The prognosis for an exophthalmos patient is contingent upon the underlying etiology and degree of the condition. Many times when the underlying condition is properly managed and treated (e. g. orbital tumours thyroid eye disease or other conditions) the prognosis is good and symptoms are manageable. If the condition is severe or left untreated, complications such as corneal damage or vision impairment may arise. This is the reason prompt medical attention is so important.
Self-care and Prevention Techniques.
To stop exophthalmos or control its symptoms
- Avoid smoking, and keep your exposure to other people's smoke to a minimum.
- To preserve moisture in the eyes and avoid dryness apply lubricating eye drops or gels as directed.
- Use safety glasses and sunglasses to help guard against light sensitivity.
- To lower the risk of complications for your eyes heed the advice of your healthcare provider regarding the management of thyroid-related conditions.
When to Get in Touch with a Medical Professional?

Make quick contact with your healthcare provider if you observe bulging eyes, particularly if the bulging is suddenly severe or accompanied by other symptoms. It is also critical to get medical help if you have a known thyroid condition such as Graves disease or if you have changes in your vision or discomfort in your eyes. The following particular circumstances should prompt you to see a doctor if you have protruding eyes:
- Abrupt onset of enlarged eyes.
- Severe bulging that produces pain in the eyes or impairs vision.
- The existence of additional symptoms like fever, redness, eye pain, or double vision.
- The well-known thyroid conditions are Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves disease. Protrusion or enlargement of one or both eyes are examples of changes in the appearance of the eyes.
Bottom Line
Exophthalmos, commonly referred to as proptosis or bulging eyes, is a sign of orbital tumours or Graves disease. Eye protrusion, dryness, double vision, and discomfort are among the symptoms that may occur. These should be evaluated by a doctor right away especially if other symptoms or a known thyroid condition accompany them.
Treatment options for strabismus vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition, ranging from self-care measures like lubricating eye drops to surgical interventions like orbital decompression or cranial surgery. Achieving positive results and averting potential complications requires early detection, appropriate management, and routine follow-ups. See your doctor straight away if you or a loved one are exhibiting symptoms.
FAQ's
What is exophthalmos?
Exophthalmos, also known as proptosis, is the medical term for bulging or protruding eyeballs.
Does exophthalmos go away?
Exophthalmos may improve over time, but this can take years, and in some cases, the eyes may continue to bulge if treatment is not received.
What causes exophthalmos in Graves' disease?
In Graves' disease, the immune system attacks the muscles and tissues around the eyes, leading to inflammation and swelling that cause the eyes to protrude.
How to treat exophthalmos?
Treatment options for exophthalmos include medications to manage thyroid function, artificial tears to lubricate the eyes, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and in severe cases, surgical interventions such as orbital decompression.
What disease causes exophthalmos?
The most common cause of exophthalmos is thyroid eye disease, particularly associated with Graves' disease.